How strength training can boost your immune system.
And cardio might have a negative effect.
(NL versie staat onderaan)
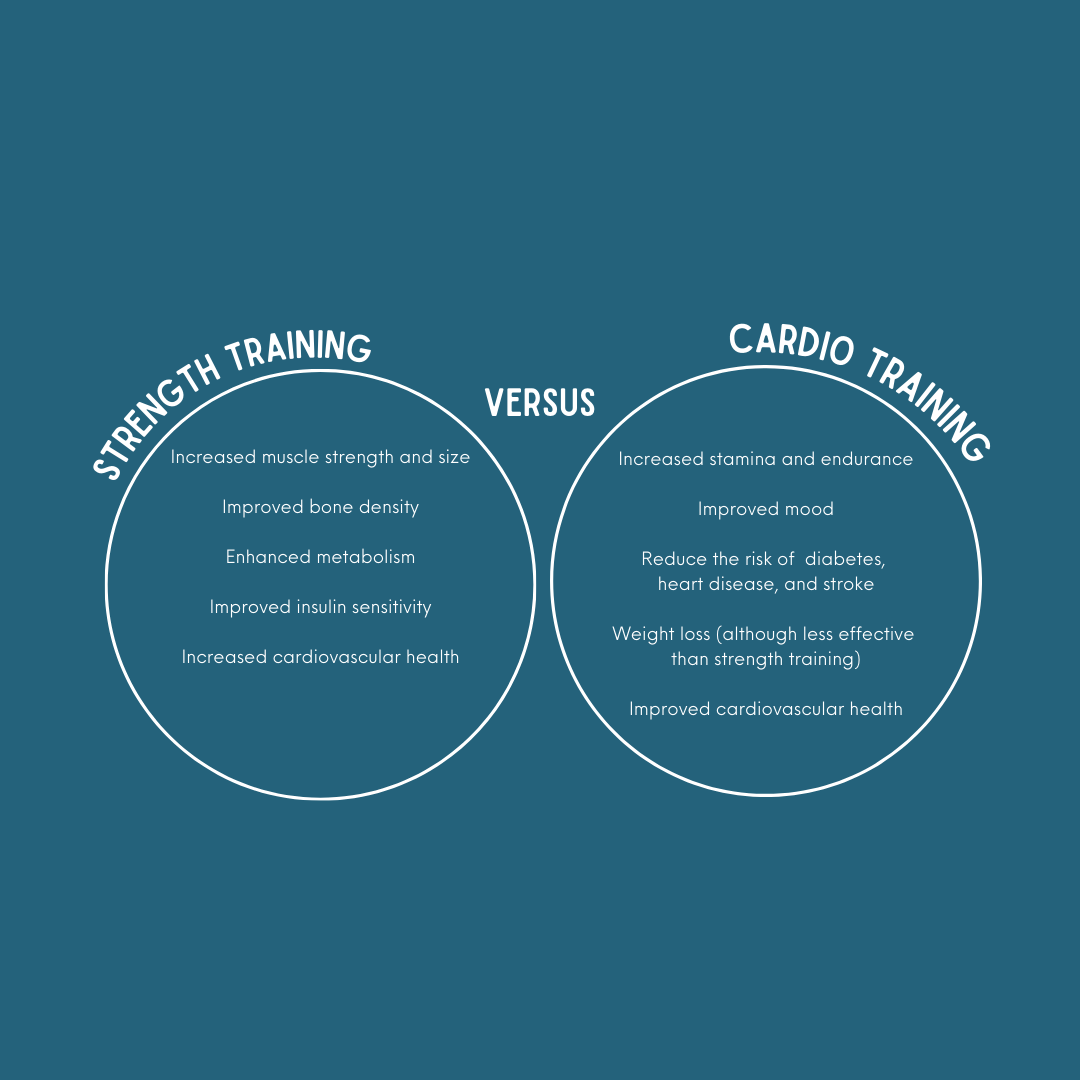
Strength training and cardio training are both important forms of exercise that can contribute to overall health and well-being. However, when it comes to boosting the immune system, there is evidence to suggest that strength training may be more effective than cardio training.
One reason for this is that strength training can lead to an increase in muscle mass, which can help to support the immune system. Muscle tissue contains immune cells, and an increase in muscle mass can lead to an increase in the number of these cells. Additionally, strength training has been shown to stimulate the production of cytokines, which are proteins that play a key role in the immune response.
Another reason why strength training may be more effective for the immune system is that it can help to reduce inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation has been linked to a range of health problems, including autoimmune disorders and chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes. Strength training has been shown to reduce inflammation in the body, which can help to support overall immune function.
Additionally, strength training can help to improve insulin sensitivity, which is important for maintaining overall health and reducing the risk of chronic disease. Insulin resistance has been linked to a range of health problems, including inflammation and impaired immune function. By improving insulin sensitivity, strength training can help to support overall immune function and reduce the risk of chronic disease.
Cardio training can also provide some benefits for the immune system, such as improving cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes. However, there is evidence to suggest that excessive cardio training can actually have a negative impact on the immune system. Long-duration, high-intensity cardio workouts have been shown to increase levels of stress hormones such as cortisol, which can have a suppressive effect on the immune system.
Overall, while both strength training and cardio training can be beneficial for overall health and well-being, there is evidence to suggest that strength training may be more effective for supporting the immune system. By increasing muscle mass, reducing inflammation, and improving insulin sensitivity, strength training can help to support overall immune function and reduce the risk of chronic disease. However, it is important to note that any form of exercise is better than no exercise, and a balanced approach that includes both strength training and cardio training is likely to provide the most benefits for overall health and well-being.
Figueiredo VC, Caldara FR, Carvalho LP, et al. Strength training boosts immunity by improving insulin sensitivity and increasing natural killer cells in breast cancer survivors. Integr Cancer Ther. 2019;18:1534735419840326. doi:10.1177/1534735419840326
This study found that strength training can boost immunity in breast cancer survivors by improving insulin sensitivity and increasing the number of natural killer cells in the body.
Gleeson M, Bishop NC, Stensel DJ, Lindley MR, Mastana SS, Nimmo MA. The anti-inflammatory effects of exercise: mechanisms and implications for the prevention and treatment of disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11:607-615. doi:10.1038/nri3041
This article reviews the anti-inflammatory effects of exercise and how these effects can help to prevent and treat disease. The authors note that strength training can reduce inflammation in the body, which can help to support overall immune function.
Simpson RJ, Kunz H, Agha N, Graff R. Exercise and the Regulation of Immune Functions. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;135:355-380. doi:10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.08.001
This article reviews the regulation of immune function by exercise and the potential mechanisms underlying these effects. The author notes that strength training can increase the production of cytokines, which are proteins that play a key role in the immune response.
Waarom krachttraining beter is dan cardio.
Krachttraining geeft je immuunsysteem een boost!
Cardio kan zelfs negatief effect hebben.
Krachttraining en cardiotraining zijn beide belangrijke vormen van lichaamsbeweging die kunnen bijdragen aan de algehele gezondheid en het welzijn. Als het gaat om het stimuleren van het immuunsysteem, zijn er echter aanwijzingen dat krachttraining effectiever kan zijn dan cardiotraining.
Een reden hiervoor is dat krachttraining kan leiden tot een toename van spiermassa, wat kan helpen om het immuunsysteem te ondersteunen. Spierweefsel bevat immuuncellen en een toename van de spiermassa kan leiden tot een toename van het aantal van deze cellen. Bovendien is aangetoond dat krachttraining de aanmaak van cytokines stimuleert, dit zijn eiwitten die een sleutelrol spelen in de immuunrespons.
Een andere reden waarom krachttraining effectiever kan zijn voor het immuunsysteem, is dat het kan helpen om ontstekingen in het lichaam te verminderen. Chronische ontstekingen zijn in verband gebracht met een reeks gezondheidsproblemen, waaronder auto-immuunziekten en chronische ziekten zoals hartaandoeningen en diabetes. Het is aangetoond dat krachttraining ontstekingen in het lichaam vermindert, wat kan helpen om de algehele immuunfunctie te ondersteunen.
Bovendien kan krachttraining helpen om de insulinegevoeligheid te verbeteren, wat belangrijk is voor het behoud van de algehele gezondheid en het verminderen van het risico op chronische ziekten. Insulineresistentie is in verband gebracht met een reeks gezondheidsproblemen, waaronder ontstekingen en een verminderde immuunfunctie. Door de insulinegevoeligheid te verbeteren, kan krachttraining helpen om de algehele immuunfunctie te ondersteunen en het risico op chronische ziekten te verminderen.
Cardiotraining kan ook enkele voordelen bieden voor het immuunsysteem, zoals het verbeteren van de cardiovasculaire gezondheid en het verminderen van het risico op chronische ziekten zoals hartaandoeningen en diabetes. Er zijn echter aanwijzingen dat overmatige cardiotraining een negatieve invloed kan hebben op het immuunsysteem. Het is aangetoond dat langdurige, zeer intensieve cardiotraining de niveaus van stresshormonen zoals cortisol verhoogt, wat een onderdrukkend effect kan hebben op het immuunsysteem.
Al met al kunnen zowel krachttraining als cardiotraining gunstig zijn voor de algehele gezondheid en het welzijn, maar er zijn aanwijzingen dat krachttraining effectiever kan zijn voor het ondersteunen van het immuunsysteem. Door de spiermassa te vergroten, ontstekingen te verminderen en de insulinegevoeligheid te verbeteren, kan krachttraining helpen om de algehele immuunfunctie te ondersteunen en het risico op chronische ziekten te verminderen. Het is echter belangrijk op te merken dat elke vorm van lichaamsbeweging beter is dan geen lichaamsbeweging, en een evenwichtige aanpak die zowel krachttraining als cardiotraining omvat, levert waarschijnlijk de meeste voordelen op voor de algehele gezondheid en het welzijn.